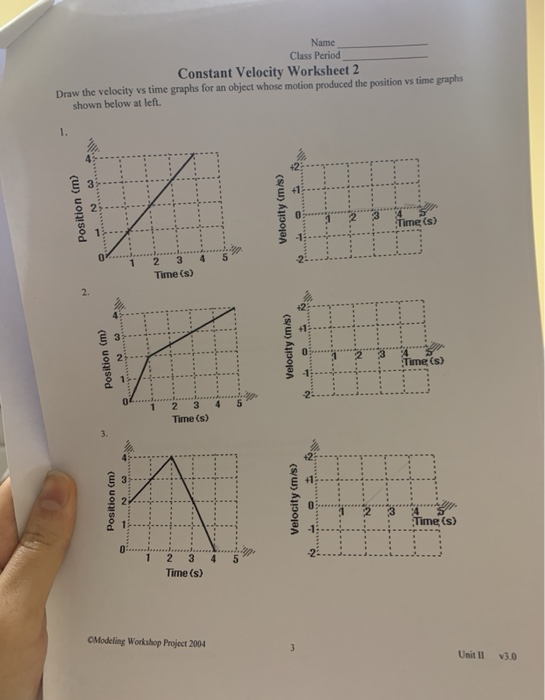
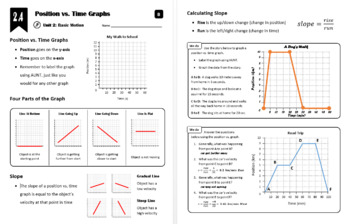
39 position and velocity vs time graphs worksheet answers
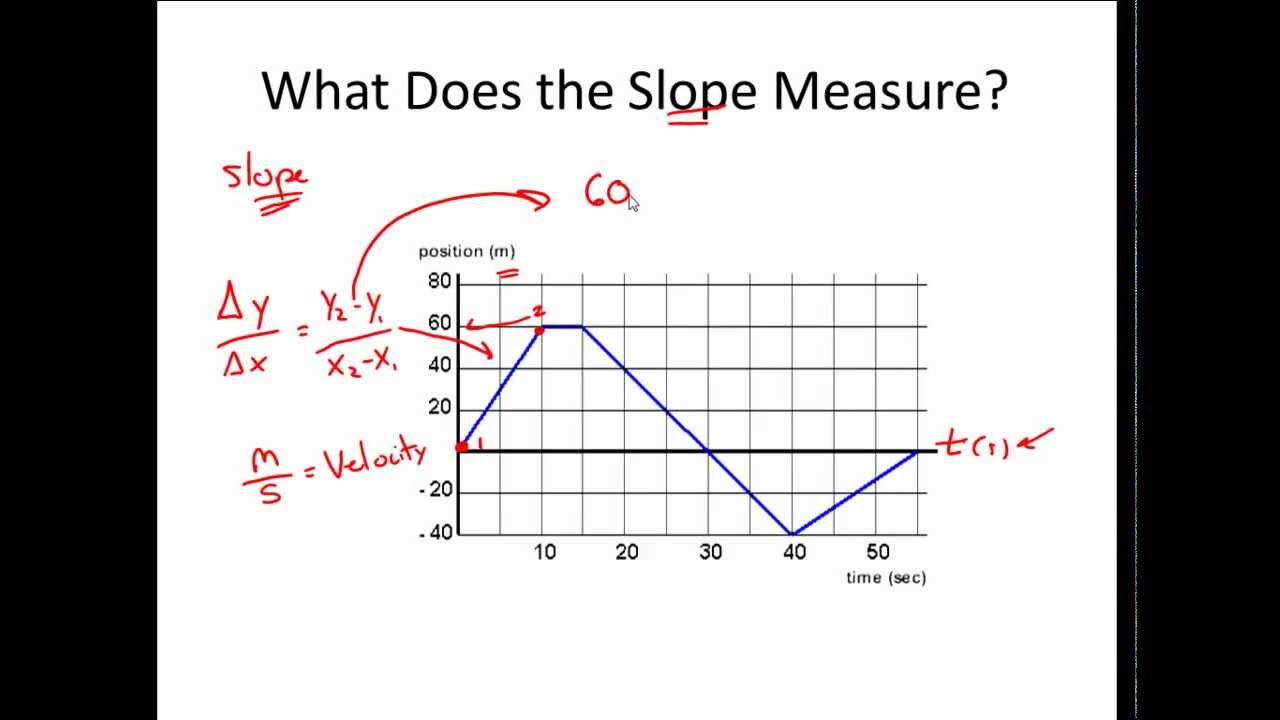
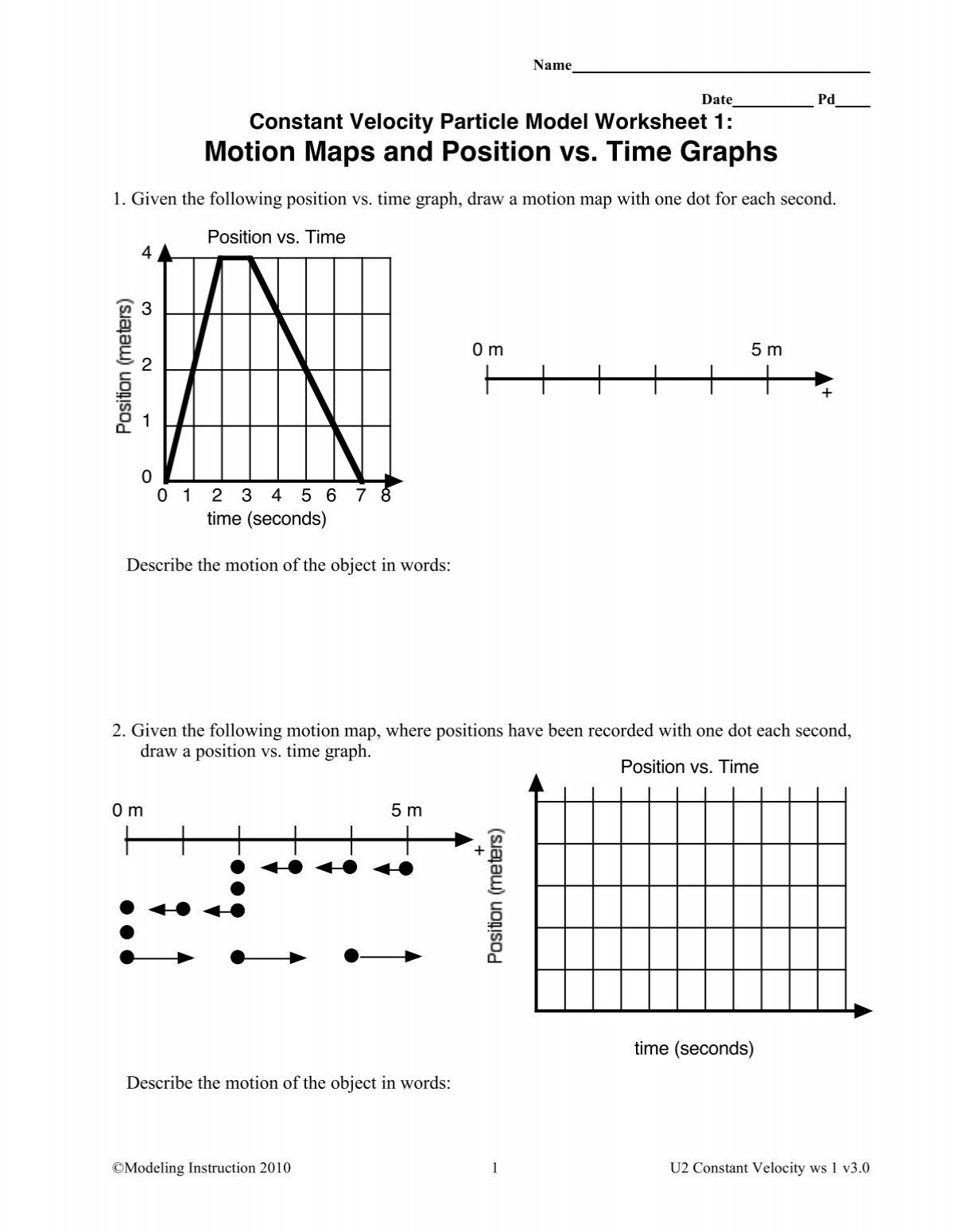
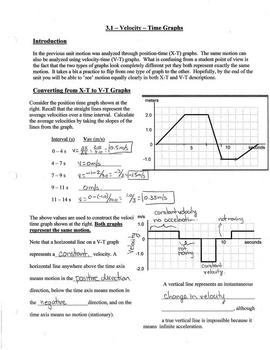
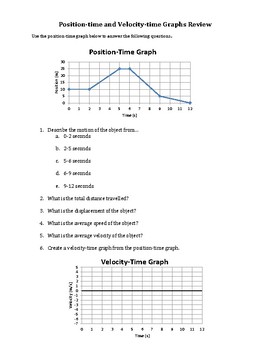
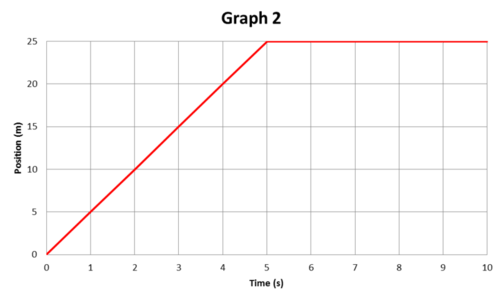
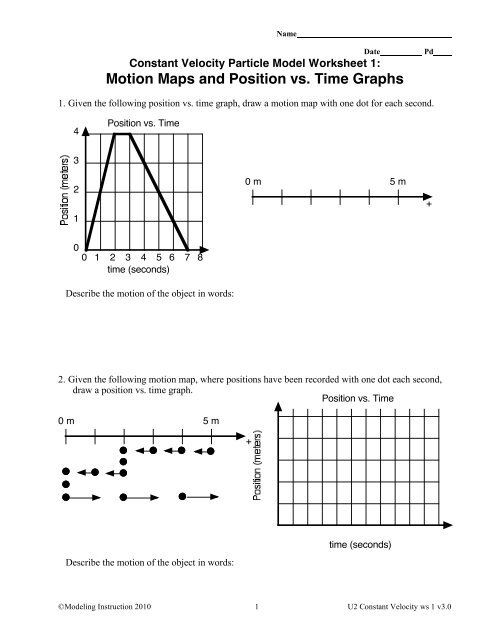
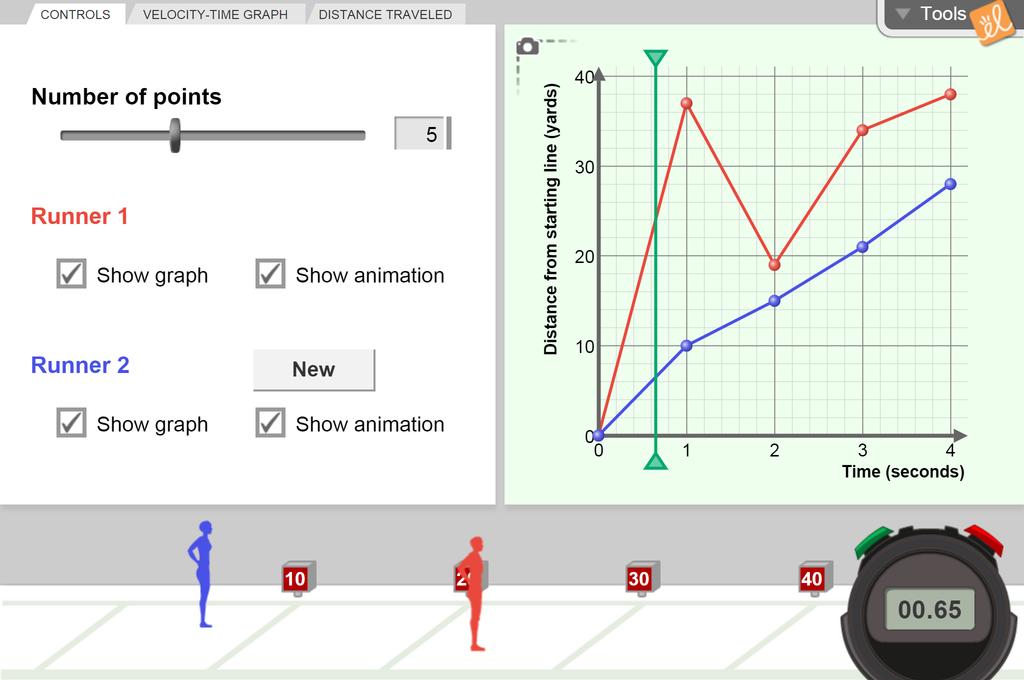
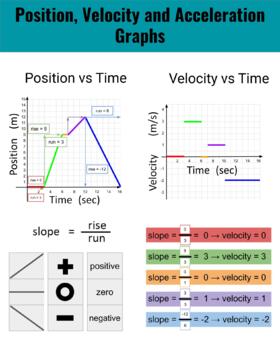
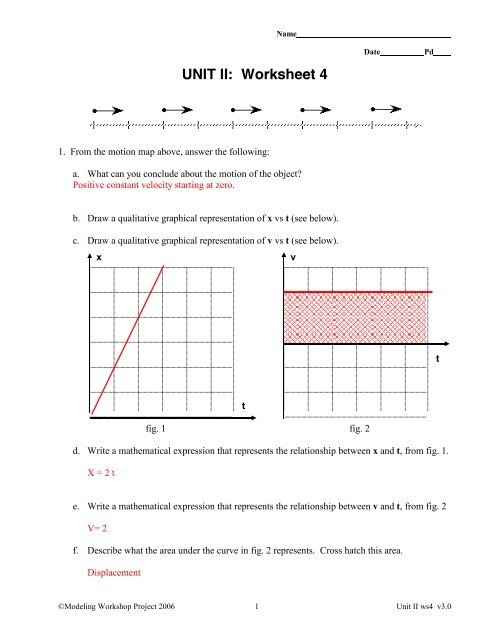
1D Kinematics Review - with Answers - Physics Classroom Position-time graphs cannot be used to represent the motion of objects with accelerated motion. The slope on a position-time graph is representative of the acceleration of the object. A straight, diagonal line on a position-time graph is representative of an object with a constant velocity. If an object is at rest, then the position-time graph will be a horizontal line located on the time … 33 Position Time Graph Worksheet Answers sekrety … They will then learn to calculate the speed and velocity from graphs. The graphs in this worksheet are high quality and easy to read. Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs Sketch velocity vs. time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object: 1. The object moves toward the ...
Vectors and Projectiles Review - with Answers - Physics Classroom The horizontal location at each 1-second instant in time is the same position as it was in the red path above it. And the vertical location at each 1-second instant in time is the same position as it was in the blue path to the left of it. The actual coordinate positions can be determined using the kinematic equations and the given time. For ...

Position and velocity vs time graphs worksheet answers
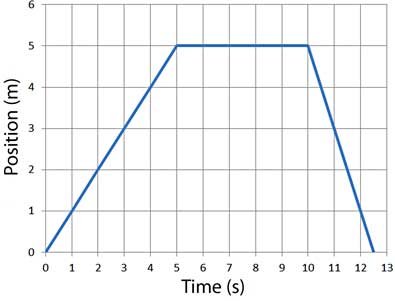
Solving for time (video) | Khan Academy Well, actually, I'll leave it like this. So you get displacement is equal to-- I can flip these around-- velocity times change in time, I should say. Or we could just say time just to keep things simple. And if you want to solve for time, you divide both sides by velocity. And then that gives you time is equal to displacement divided by ... Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time ... Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs Sketch velocity vs. time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object: 1. The object moves toward the origin at a steady speed for 10s, then stands still for 10s. There are 2 possibilities: a) (in red ) object moves toward origin in positive direction so it starts on negative … Kinematic Equations: Sample Problems and Solutions - Physics … Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations. This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and …
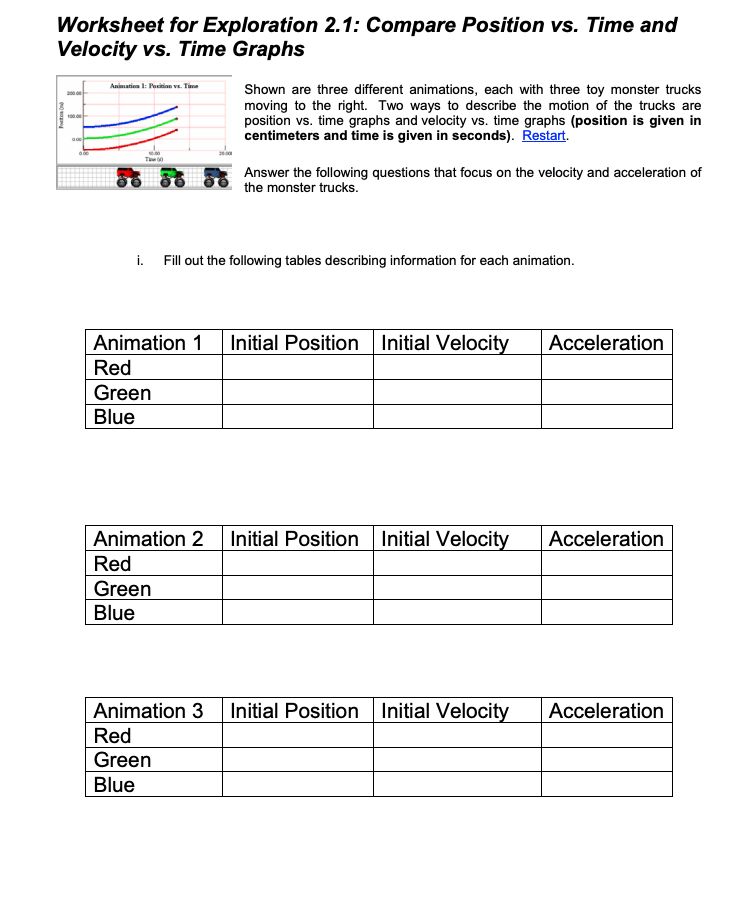
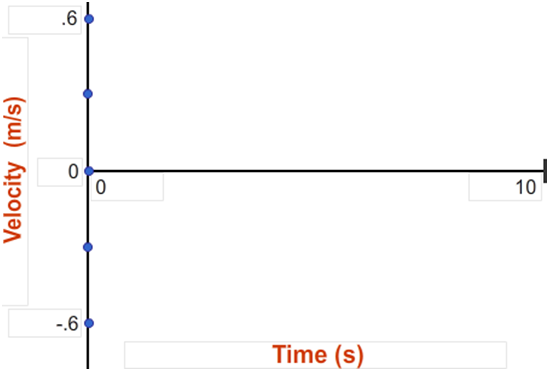
Position and velocity vs time graphs worksheet answers. Grade 8 science teacher's guide - SlideShare 2. Aug. 2015 · It states that, “An object will stay at rest or move at constant velocity unless an unbalanced external force acts on it.” If time permits, discuss also the effect of mass on inertia: the greater the body’s mass, the greater will be its inertia. For the application part, relate the concept of inertia to students’ experiences while riding a vehicle. Then discuss the importance … velocity and acceleration graphs worksheet answers Web. 1.3 Create and interpret graphs of 1-dimensional motion, such as position vs. time, distance vs. time, speed vs. time, velocity vs. time, and acceleration vs. time where acceleration is constant. Understanding the definitions of velocity and acceleration allows us to create graphs which illustrate the motion. The mathematical definitions are as. Kinematic … Principles and Standards - National Council of Teachers of … A comprehensive and coherent set of mathematics standards for each and every student from prekindergarten through grade 12, Principles and Standards is the first set of rigorous, college and career readiness standards for the 21st century. Principles and Standards for School Mathematics outlines the essential components of a high-quality school mathematics program. The Moving Man - Position | Velocity | Acceleration - PhET Learn about position, velocity, and acceleration graphs. Move the little man back and forth with the mouse and plot his motion. Set the position, velocity, or acceleration and let the simulation move the man for you.
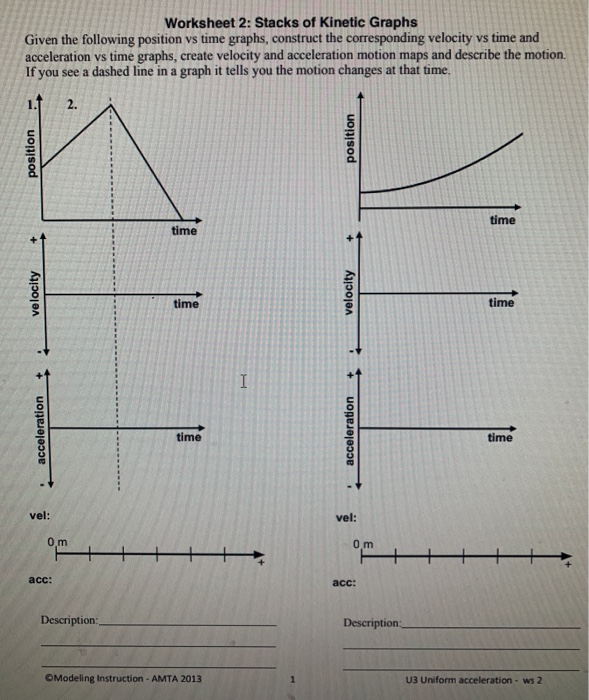
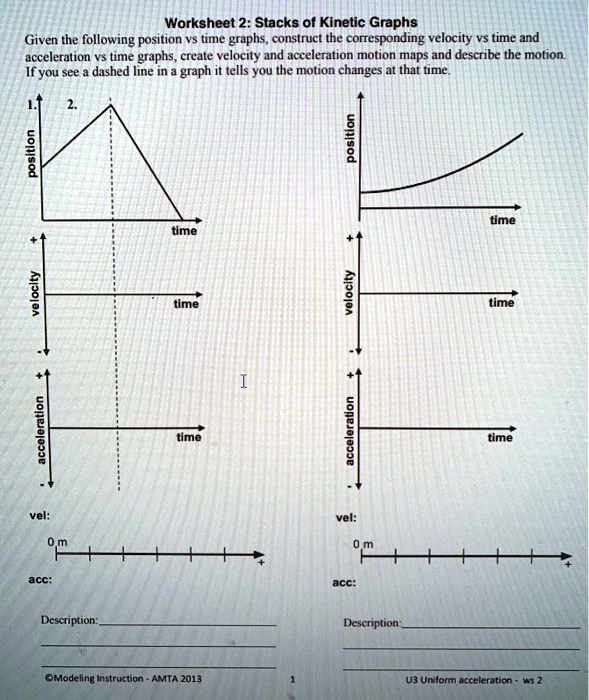
Kinematic Equations: Sample Problems and Solutions - Physics … Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations. This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and … Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time ... Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs Sketch velocity vs. time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object: 1. The object moves toward the origin at a steady speed for 10s, then stands still for 10s. There are 2 possibilities: a) (in red ) object moves toward origin in positive direction so it starts on negative … Solving for time (video) | Khan Academy Well, actually, I'll leave it like this. So you get displacement is equal to-- I can flip these around-- velocity times change in time, I should say. Or we could just say time just to keep things simple. And if you want to solve for time, you divide both sides by velocity. And then that gives you time is equal to displacement divided by ...














0 Response to "39 position and velocity vs time graphs worksheet answers"
Post a Comment